Welcome Oracle Retail fans. In this article, we'll be exploring all about RMS Stores and Warehouse Locations. This is a sub-article on RMS, for complete detail on RMS, you may want to refer to parent article Oracle Retail Merchandising Systems - Deep Dive
Store
Store is the lowest level of the organizational hierarchy. A Store in RMS is the actual retail location and is considered a stock holding location for the Brick and Mortar channel. Store is the level at which all business transactions occur.
When creating a new store, the user will enter basic information like Store ID, Name, District, and Address. In addition to that a Like Store can be selected and an existing store’s items’ cost, retail, and replenishment parameters (if required) are copied to the new store. A batch job then adds the store into RMS. Note: Like Store functionality does not copy clearance skus to the new store.
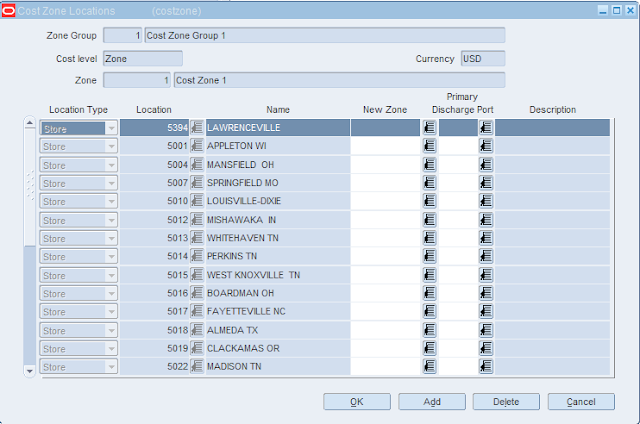
• Defines the physical retail location/s. Store can be Stock Holding/Non Stock Holding location.
• One store will only belong to one district
• The application allows up to a ten digit id
• Level at which all business transactions occur:
• Sales
• Returns
• Receipts
With RMS becoming the system of record for stores, only merchandising attributes related to functionality being used in RMS will be stored in RMS. Store attributes related functionalities that will be used are described in the next few paragraphs.
Store Address
RMS requires two mandatory addresses for each store – Business address and Postal address. Other address types as required by business can be added as well.
Store Custom Attributes
RMS allows the addition of new attribute definitions that are specific to a retailer. These new attributes are defined after determining that those are truly required by the retailer and after, are added into the system by the system administrator. Afterwards, users can store values in those attributes e.g. Longitude, Latitude, Departments available at that Store, Store Hours and Eligibility to do Ship-to-Store.
Store Format
RMS Store Format functionality allows defining the store formats that can be applied to the stores in the organization. Some examples are Mall, Strip Mall, and Kiosk. After the formats are defined, stores in the organization can be associated with a format.
Store Department Area
This functionality allows storage of the square foot area dedicated to a given department within a given store as of an effective date.
Stop Ship (Distribution Stop)
This functionality allows Retailers to indicate when specific stores should not receive items of a particular department, class and subclass combination. This is normally used in conjunction with Allocation system.
Activity Schedule
This functionality keeps information about store availability on specific dates for shipments, receiving and sales. It can also be used for the temporary closing of stores (for reasons like fire, flooding or remodel) so that the store is taken out of comparison calculations.
Transfer entity
Transfer entities define which locations in an organization are grouped together due to legal requirements. Transfer entities can be defined by brand, geography, country or other grouping defined by your company. Moving items between transfer entities is treated as a sale from the sourcing location and purchase by the receiving location.
Transfer zones
Transfers zones are the grouping of locations within an area. Transfer zones are set up to restrict the transfer of items to locations within the transfer zone
Other Store Attributes
Following are the other notable store related functionalities available in RMS. Let me know if you need more details for any of these:
1. Maintenance of Competitive Store for competitive shopping purposes.
2. Maintenance of POS Configuration like Coupon, Money Orders, Product restriction, Pay in /pay out, Supplier Payment Type, Tender Type and Touch buttons for downloading to POS registers.
3. Store Class attribute where stores are attached to one of the store classes – A, B, C, D and E that typically classifies stores by the size (ranking by volume).
4. RMS can have Store Grade data interfaced to it from planning systems. Store grade is typically then fed to Allocation systems.
5. Delivery Schedule functionality allows management and maintenance in RMS of delivery schedules from either a warehouse or from a supplier to store.
6. Geocode data is used for tax functionality.
7. Default warehouse – default sourcing warehouse for Store for the purpose of replenishing items
8. Store open/close – Store Open and Closed Date
9. VAT regions (value added tax) – VAT Regions for the Store
10. Store attributes – additional attributes may include warehouse, bank, accounting, location, and pharmacy information
11. Location traits - Location traits are a means of grouping stores together used for Sales Audit (ReSA)
12. Address
13. Email address
14. Store order dates
15. Duns number
16. Channel ID
2. Warehouses in RMS (incl. Virtual and physical)
A warehouse is a physical storage, cross-dock or distribution facility. A warehouse has all transaction capabilities of a store, except for the ability to sell. The warehouse will no longer be defined as a store but will be established as a physical warehouse within RMS. In RMS, the warehouse does not need to be part of the 6 levels of the Organization Hierarchy. The reason for this feature is that a warehouse has the ability to ship merchandise across the entire company’s organizational hierarchy.
· Defines a physical storage, cross-dock, and/or distribution facility
· Level at which business transactions occur, except sales
· Can be optionally tied to any level of the organizational hierarchy for reporting
· Activity schedule for shipping and receiving can be defined
· The application allows up to 10 digit warehouse numbers
Stock holding indicators –warehouses
Virtual warehouse
· Allows the retailer to have 1 physical warehouse that stocks many virtual warehouses.
· A physical warehouse can have one or more virtual warehouses associated with it and is considered a “non-stock holding” location because the virtual warehouses are the “stock holding” entities.
· RMS expects a Warehouse Management System to hold warehouse related attributes and hence the number of attributes maintained in RMS is very limited. Attributes that are maintained in RMS are as follows:
WH Address
RMS requires two mandatory addresses for each warehouse – Business address and Postal address. Other address types as required by the business can be added as well.
WH Attribute
Total square footage, a number of loading/unloading docks and time zone are maintained here.
Activity Schedule
This functionality keeps information about warehouse availability on specific dates for shipments and receiving.